When dealing with objects and data, there are times you need to put the data in a specific order, such as alphabetical. There are various ways to go about sorting.
You could loop through an array, for example, and do some comparisons and swap data around as needed. So, while this is possible, it can be complex and prone to errors. Thankfully, JavaScript helps us out with a built-in sorting method…sort().
Note: keep data type in mind when sorting. For example, dates. Is a date an actual date or a string representation of a date? Comparing dates can sometimes be tricky. JavaScript has a date object method to create dates, which represents the date in milliseconds.
Here is an example…imagine you have the following array…
// Create animals array var animals = ["Lions", "Tigers", "Bears", "Badgers"]; // Output array to the console console.log(animals);
Here is a screenshot of the output…
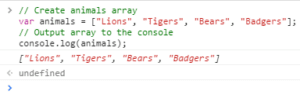
Now let’s sort our animals…
// Create animals array var animals = ["Lions", "Tigers", "Bears", "Badgers"]; // Sort the array of animals animals.sort(); // Output array to the console console.log(animals);
Here is the result…
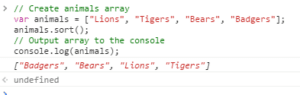
As you can see, sorting is fairly straightforward. You should know that the sort method can take an optional parameter. The optional parameter would be a compare function to perform custom sorting. In other words, you can define an alternative sort order. Whatever compare function gets passed in, it needs to return a negative, positive or zero value. This tells the sort method how to order the items.
// Compare function
function(a, b){
return a-b
}
Using a compare function like above, the sort method will compare the two values. It then sends the values to the compare function, sorts the values according to the returned value (negative. positive or zero).
So imagine you are comparing two numbers…5 & 10. In a regular sorting scenario, you would have 5 come before 10. The sort function gets passed the numbers (5 & 10), does a simple subtraction (5 – 10 = -5) and sees that it is a negative value. So 5 should come before 10.
Happy Coding!
Clay Hess



